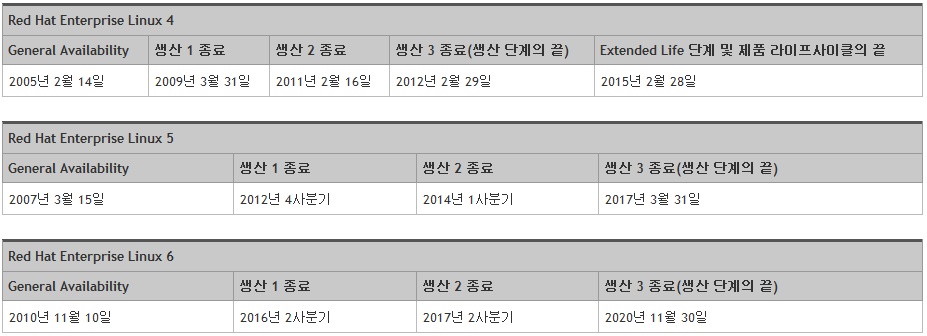
Redhat의 RHEL4가 생산이 중단이 되었습니다. 즉 더이상 커널 패치 및 어플 패치를 제공하지 않는다는 것입니다.
https://access.redhat.com/support/policy/updates/errata/
같은 RPM을 사용하고 있는 CentOS4의 경우에는 같은 운명을 가지고 있습니다.
아래의 사이트에서 보면 http://vault.centos.org/4.9/ 에서 마지막 패키지를 제공하고 있습니다.
http://lists.centos.org/pipermail/centos-announce/2012-February/018462.html
하지만 아직도 여전히 많은 시스템들이 CentOS 4 기반으로 운영이 되고 있기 때문에 2012년 2월까지 만들어진 패키지를 이용해서 추가 설치를 할수 있어야 합니다. 하지만 기존의 설정을 그대로인 상태에서 패키지 관리자인 yum을 사용하게 되면 아래와 같은 에러로 사용을 할수가 없는 상황입니다.
[root@localhost ~]# yum list Setting up repositories not using ftp, http[s], or file for repos, skipping - 4 is not a valid release or hasnt been released yet Cannot find a valid baseurl for repo: update Error: Cannot find a valid baseurl for repo: update [root@localhost ~]#
이런 경우에는 아래와 같이 /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo 파일을 수정해서 사용하면 됩니다.
(참고: https://www.centos.org/modules/newbb/viewtopic.php?topic_id=36528&forum=27)
[localhost(root):/etc/yum.repos.d]# diff -Nu CentOS-Base.repo.120418 CentOS-Base.repo --- CentOS-Base.repo.120418 2012-04-18 10:47:11.000000000 +0900 +++ CentOS-Base.repo 2012-04-18 10:50:12.000000000 +0900 @@ -13,8 +13,9 @@ [base] name=CentOS-$releasever - Base -mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os +#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os #baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/ +baseurl=http://vault.centos.org/4.9/os/$basearch gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-centos4 priority=1 @@ -23,8 +24,9 @@ #released updates [update] name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates -mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates +#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates #baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/ +baseurl=http://vault.centos.org/4.9/os/$basearch gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-centos4 priority=1 @@ -33,8 +35,9 @@ #packages used/produced in the build but not released [addons] name=CentOS-$releasever - Addons -mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=addons +#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=addons #baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/addons/$basearch/ +baseurl=http://vault.centos.org/4.9/os/$basearch gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-centos4 priority=1 @@ -43,8 +46,9 @@ #additional packages that may be useful [extras] name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras -mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras +#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras #baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/ +baseurl=http://vault.centos.org/4.9/os/$basearch gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-centos4 priority=1 @@ -53,8 +57,9 @@ #additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages [centosplus] name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus -mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus +#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus #baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/ +baseurl=http://vault.centos.org/4.9/os/$basearch gpgcheck=1 enabled=0 gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-centos4 @@ -64,8 +69,9 @@ #contrib - packages by Centos Users [contrib] name=CentOS-$releasever - Contrib -mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib +#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib #baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/contrib/$basearch/ +baseurl=http://vault.centos.org/4.9/os/$basearch gpgcheck=1 enabled=0 gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-centos4 [localhost(root):/etc/yum.repos.d]# |
저는 이렇게 해서 기존의 CentOS에서 jar 파일을 생성하기 위해서 java-1.4.2-gcj-compat-devel-1.4.2.0-27jpp 패키지를 yum으로 설치하여 jar 프로그램을 사용할 수 있었습니다.